China buys 49% of ACWA Power renewables; US to build concrete thermal storage plant
Our pick of the latest solar thermal news you need to know.

Related Articles
China's Silk Road Fund acquires 49% of ACWA Power Renewable Energy
China's Silk Road Fund has purchased a 49% stake in ACWA Power Renewable Energy (ACWA Power RenewCo), the Saudi Arabian group announced June 23.
ACWA Power is a leading solar and wind developer in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) and the dominant developer of CSP plants in the region.
ACWA Power RenewCo owns 1.7 GW of PV, CSP and wind assets across the United Arab Emirates (UAE), South Africa, Jordan, Egypt and Morocco, the company said.
ACWA Power had already signed several strategic renewable energy agreements with Chinese groups and the Silk Road Fund is a major shareholder in ACWA Power's $4.4 billion Noor Energy 1 CSP-PV project in Dubai, UAE.
ACWA Power signed a record-low power purchase price of $73/MWh for the project with the Dubai electricity and water authority (DEWA), which will own half of the project equity.
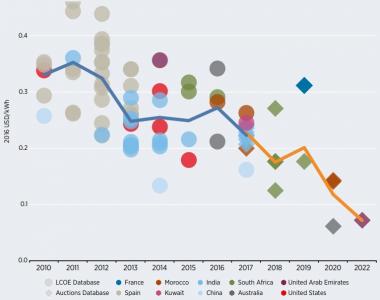
CSP levelized cost, auction price trends
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: International Renewable Energy Agency (Irena), January 2018.
Currently under construction, the 950 MW Noor Energy 1 project will include three 200 MW parabolic trough CSP systems, a 100 MW CSP tower plant, 250 MW of PV capacity and 15 hours of molten salt CSP storage capacity. Shanghai Electric is the contracted Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) supplier.
ACWA Power has also been a key player in Morocco, where it has developed three CSP projects for a total capacity of 510 MW and three PV plants for a capacity of 177 MW.
Spain's Refractaris to supply heat shield for Dubai’s Noor Energy 1
Spanish group Refractaris is to supply the thermal heat shield for the CSP tower section of the 950 MW Noor Energy 1 CSP-PV plant in Dubai, UAE, Refractaris said in a statement.
Developed by ACWA Power, the 950 MW Noor Energy 1 project will include three 200 MW parabolic trough CSP systems, a 100 MW CSP tower plant, 250 MW of PV capacity and 15 hours of molten salt CSP storage capacity.
Shanghai Electric is the contracted Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) supplier and the project will include technologies from a wide range of European and U.S. suppliers.
Spain's Abengoa will supply the parabolic trough systems and Lointek will supply the integrated steam generation system and oil-salt thermal storage system. Belgium's CMI will supply the molten salt receiver for the tower plant and Rioglass will supply the heliostats, while U.S. technology developer BrightSource will supply the control systems for the tower plant section. Germany's Siemens will supply four steam turbine generators and auxiliary equipment for the parabolic trough and tower plants. Denmark's Aalborg will supply steam generation technology for the parabolic trough section.
Refractaris has previously supplied heat shields for the 110 MW Cerro Dominador CSP tower project in Chile and the 50 MW Luneng Haixi Project in China.
For Noor Energy 1, Refractaris signed its supply agreement with Shanghai Boiler Work, which is responsible for the construction of the tower receiver.
The Noor Energy 1 plant will be brought online in phases in 2020-2022 and the first parabolic trough plant and central tower unit are currently on schedule to be completed by October 2020.
US to develop commercial-scale concrete thermal storage
The U.S. Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) is to lead a $5-million research project to develop concrete thermal energy storage (CTES) technology that could be used in CSP and conventional power plants, EPRI announced July 1.
"Concrete thermal energy storage has the potential to be significantly cheaper than batteries with a smaller footprint. It also has the potential for longer-duration storage, which will be critical as more wind and solar come on-line," EPRI said.
The CTES system transports high-pressure steam from power plants through tubes, heating and storing the modules ready for conversion to electricity.
Funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), EPRI and its project partners will design and build a pilot 10 MWh CTES system which will be integrated into an existing coal plant for testing.
"The testing will establish the capabilities of the CTES system in a real-world environment, demonstrating its efficiency and ability to handle flexible operating conditions. In addition, an analysis will be done to determine the costs and benefits of a full-scale application of CTES technology," EPRI said.
Partners in the project include CTES technology developer Bright Generation Holdings, engineering group AECOM and power utility Southern Company.
AECOM will supply engineering procurement and construction (EPC) resources and Southern Company will provide the field test site and operational support.
Initial work on the project will start in October and the pilot system is expected to be operational by early 2021.
New Energy Update