US wind support not driving coal closures; E.ON enters UK, Italy O&M markets
Our pick of the latest wind power news you need to know.

Related Articles
US study says wind, solar support not main driver of coal, nuclear closures
Low U.S. natural gas prices and flat demand for electricity are the main drivers behind the closure of some coal and nuclear power plants, rather than state and federal policies supporting renewable energy projects, according to a report by consulting firm Analysis Group commissioned by the Advanced Energy Economy (AEE) group and the American Wind Energy Association (AWEA).
AEE and AWEA commissioned the report after Energy Secretary Rick Perry ordered a study of the electricity grid to determine whether support for solar and wind energy is accelerating the retirement of coal and nuclear facilities. The government's 60-day study is expected to be published in the coming weeks.
In its report, the Analysis Group said current wholesale market frameworks and support measures for renewable energy do not appear to be significant drivers of coal and nuclear power plant closures.
Fundamental market forces such as flat demand for electricity, low natural gas prices since the mid-2000s and the addition of significant amounts of highly efficient new gas-fired resources since 2000, are primarily responsible for impacting the profitability of merchant generating assets, the report said.
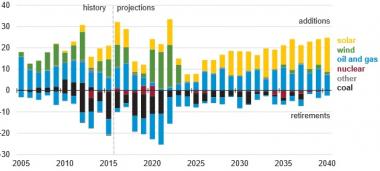
Forecast US generation capacity additions
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: EIA's Annual Energy Outlook 2017.
"The Analysis Group report has now been submitted to the U.S. Department of Energy to inform its review," AEE and AWEA said in a statement.
E.ON expands wind O&M business into UK, Italy
Germany's E.ON has expanded its wind operation and maintenance (O&M) business into the UK and Italy, where warranty periods for many installations are set to expire, the company said in a statement.
The UK and Italy have a combined installed wind capacity of 25 GW. E.ON has been active in the US and Swedish wind services markets since 2015 and the company rolled out its wind services business in Germany at the start of this year.
E.ON provides its O&M services through its subsidiary E.ON Climate & Renewables. The services include site management, windfarm optimization, and major maintenance work.
The levelized cost of energy (LCOE) of wind power has fallen on greater turbine efficiency and O&M market competition between original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), independent service providers (ISPs) and operator in-house teams.
E.ON has adopted a "mix" of O&M strategies for its own 5.3 GW global wind power fleet, which includes 3.2 GW of U.S. capacity and 2.1 GW in Europe, Roland Flaig, Head of Wind Operations- Onshore Europe, at E.ON Climate & Renewables, said in February.
The company has used “Hands-on” supplier-operator partnerships to improve windfarm operations and greater knowledge-sharing between partners along with data analytics and smart maintenance could see wind LCOE fall to as low as 30 euros/MWh, Flaig said.
In the U.S., the expiry of U.S. Production Tax Credits (PTCs) for ageing turbines and the gradual removal of PTC support for new projects have prompted operators to re-examine O&M activities.
The wind power industry must optimize service contracts and operational practices to take into account the falling revenues and rising costs of ageing turbines, Patrick Woodson, E.ON Chairman, North America, said in April.
"There is an emerging mismatch between availability and profitability which are not really in the owner's interests...We have to look at the evolution of the revenues over time and see how we can maximize these projects," he said.
Windfarm revenues can drop by a third following the removal of the PTC and many of these facilities are also outside the window for acquiring a power purchase agreement (PPA), Woodson noted.
"By the end of 2017 we are going to have 20 GW of projects which no longer have any PTC values, most of which are facing extremely low power prices. It's going continue to be a big challenge for all of us," he said.
Global wind capacity forecast to rise fourfold by 2040
Global installed wind capacity is forecast to increase fourfold by 2040 and wind and solar power will together account for 48% of global installed capacity by 2040, compared with 12% currently, Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) said in its New energy Outlook 2017 report.
"We anticipate renewable energy reaching 74% penetration in Germany, 38% in the U.S., 55% in China and 49% in India by 2040 as batteries and new sources of flexibility bolster the reach of renewables," BNEF said.
Some $3.3 trillion will be invested in wind power generation between now and 2040, according to the report. Wind investment is expected to grow faster than solar, rising 3.4% per year compared with 2.3% for solar.
Top 10 wind installation countries in Jan-Dec 2016

Source: Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC).
Global power demand is expected to grow by 58% between now and 2040 but power demand growth will decouple from GDP, BNEF said.
"We expect the intensity of electricity consumption per unit of GDP to fall by 27% over 2016-40," it said.
BNEF's projections are based on industry drivers that prompt rapid change in markets and business models. These drivers include the cost of renewable energy and storage technology, electricity demand and outlooks for electricity vehicle deployment.
The medium to long term forecast is driven by the cost of building different power generation technologies to meet projected peak and average demand, by country. The model deploys least-cost technology options in line with shifting capital, operating and financing costs.
New Energy Update